Recently, a research team led by Academician Huang Wei and Professor Lai Wenyong from the National Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics/School of Chemistry and Life Sciences at Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (NJUPT), in collaboration with international institutions such as Hong Kong Baptist University and the National University of Singapore, has achieved a milestone in the field of nonlinear optics in organic semiconductors. The team innovatively proposed a theoretical model of “spectral-tunable gain-induced Raman lasing”, revealing the core mechanism of resonance matching between molecular vibrations and stimulated emission. For the first time, they successfully achieved exponential amplification of Raman signals and efficient multi-order Raman lasing in organic semiconductor materials—without relying on complex optical microcavity structures. This research breaks through the bottleneck of traditional nonlinear optical theory, which assumes “weak molecular vibrational gain and dependence on high-energy pumping”, laying a theoretical foundation for expanding the application of organic semiconductors in nonlinear optics, particularly in Raman lasers. It also provides new ideas and methods for developing flexible Raman lasers and enabling high-precision sensing and detection. The study, titled Giant nonlinear Raman responses from organic semiconductors, has been published in the prestigious journal Nature Materials (2025, DOI: 10.1038/s41563-025-02196-9).

Nature Materials published the latest research by Academician Huang Wei and Professor Lai Wenyong’s team
Organic semiconductors, with their unique molecular structures and optoelectronic properties, are regarded as core materials for next-generation flexible electronics, widely applied in flexible displays, photovoltaics, and other fields. However, their nonlinear optical effects typically require extremely high-energy excitation, leading to material damage under intense light, which has long limited their application in nonlinear optics. Raman scattering, a nonlinear optical technique based on molecular vibrations that generates optical gain, holds significant potential in explosives detection, bioimaging, and optical communications due to its characteristic molecular vibrational signals and spectral tunability. Traditional Raman lasing relies on high-energy pump sources to overcome molecular vibrational losses, resulting in bulky and costly setups. Achieving “low-threshold, high-gain” Raman lasing has remained a global scientific challenge.
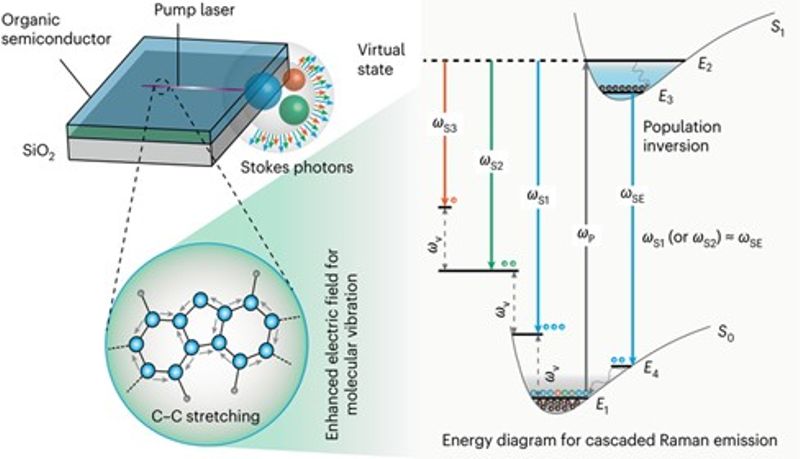
Resonance matching between stimulated emission and Raman scattering
To address this challenge, the research team explored the synergistic coupling mechanism of quantum optics and molecular vibrations, proposing a theory of resonance matching between stimulated emission and Raman scattering. They developed a novel “spectral-tunable gain-induced Raman lasing” method, successfully realizing exponential amplification of Raman signals. The Raman optical devices fabricated using this method exhibit ultra-low thresholds (20–50 μJ/cm2), four orders of magnitude lower than existing mainstream Raman lasers. The Raman lasing signals demonstrate exceptionally strong energy output, with a signal-to-noise ratio exceeding 30 dB, and achieve cascaded Raman signals with a bandwidth of over 110 nm. The devices show remarkable sensitivity in explosives detection, achieving detection sensitivities above 95% and 80% for dinitrotoluene (DNT) and trinitrotoluene (TNT), respectively, at concentrations as low as one part per billion in air.
This groundbreaking discovery overturns the traditional nonlinear optics paradigm of “high energy for high gain” and has been highly praised by international peer reviewers, who noted that the study opens a new perspective to perfectly address the worldwide challenge of insufficient Raman gain and is expected to reshape the direction of Raman lasing research, with broad applicability across different material systems. The findings expand the application scenarios of organic semiconductors, pioneering a new direction for organic semiconductor Raman lasers and reinforcing China's leading position in flexible electronics and photonics. This technology holds promise for applications in visible-light communications, portable real-time explosives detection, and wearable non-invasive health monitoring.
Academician Huang Wei and Professor Lai Wenyong from NJUPT’s National Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics/School of Chemistry and Life Sciences, Professor Xie Guowei from Hong Kong Baptist University, and Academician Liu Xiaogang from the National University of Singapore served as co-corresponding authors. Professor Jiang Yi, graduate students Lin He, and Pan Jinqiang from the same institution are co-first authors. Professor Ifor Samuel from the University of St Andrews provided assistance and suggestions for data analysis. The research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
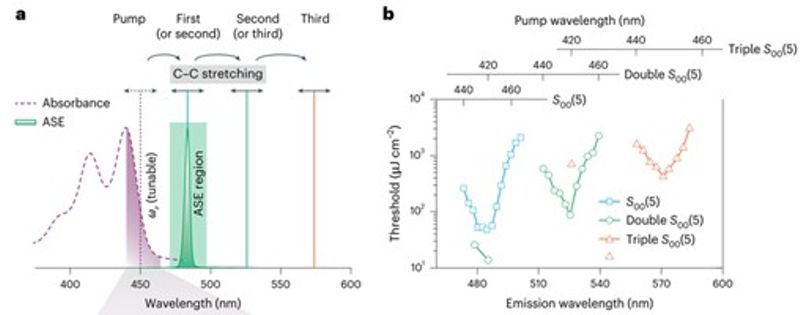
Spectral tuning characteristics of cascaded Raman lasing
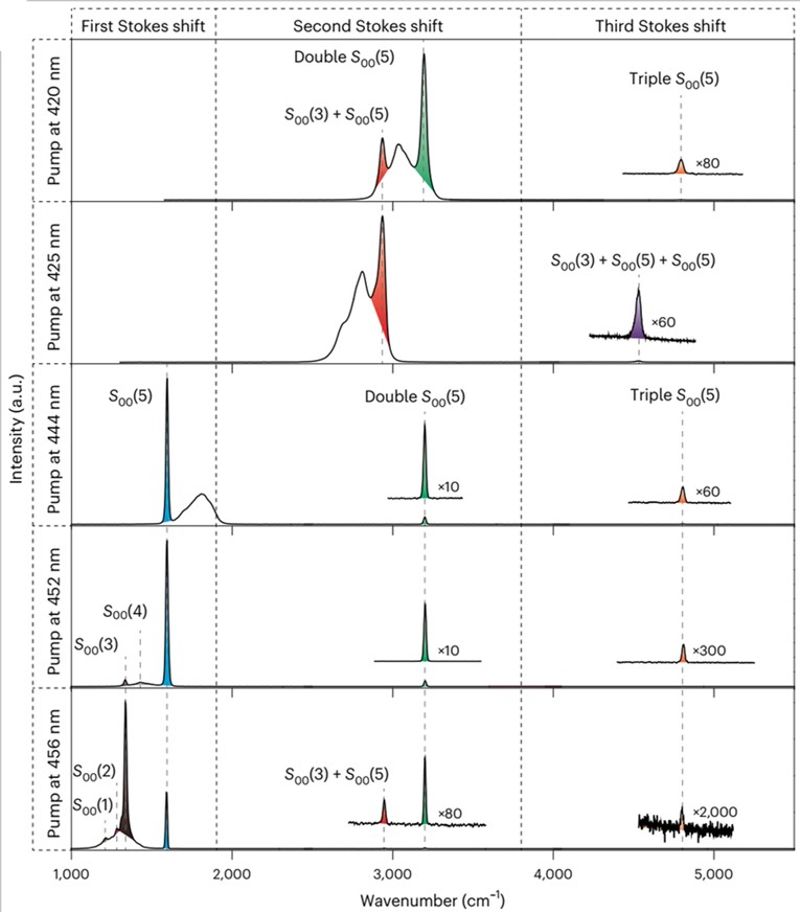
Spectra of cascaded Raman lasing
Original article link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-025-02196-9
(Author: Jiang Yi; Initial Review: Qiao Zuqin, Luo Zhimin, Dai Xiubin; Editor: Wang Cunhong; Final Review: Zhang Feng)



